A Quick Guide to Seasonal Allergies
Pollen, Grass, Ragweed and Mold spores
For more than 24 million Americans, the flowering trees and mild weather of spring and summer, signals another allergy season in full bloom. The cause: substances such as pollen, grass, ragweed and mold spores enter the body and are mistakenly identified as a threat by the immune system, triggering a variety of symptoms. We hope you find some comfort in this quick guide to seasonal allergies.
Reduce the effects of seasonal allergies
- Pollen and spores can be carried into the home on your clothes or enter through windows during allergy season.
- Know which pollens you are sensitive to and then check pollen counts. Weather reports often include this information during allergy seasons. In spring and summer, during tree and grass pollen season, levels are highest in the evening. In late summer and early fall, during ragweed pollen season, levels are highest in the morning. For an interactive map to view allergy levels and pollen count forecasts, visit pollen.com.
- If your allergy symptoms are very bothersome:
1. Take a shower, wash your hair and change your clothes after you’ve been working or playing outdoors, and keep windows and doors shut at home and in your car.
2. Wear sunglasses and a hat outside to keep pollen out of eyes and hair. Your COVID-19 mask could provide a protective barrier against pollen.
3. Indoors, get an air purifier with a HEPA filter, and vacuum regularly.
Treatment
Seasonal allergies are treated with over-the-counter or prescription antihistamines (non-drowsy types are available), nasal steroid spray, decongestants and immunotherapy (allergy shots that expose you over time to gradual increments of the allergen), as well as alternative methods. Please check with your healthcare provider to discuss what’s right for you.
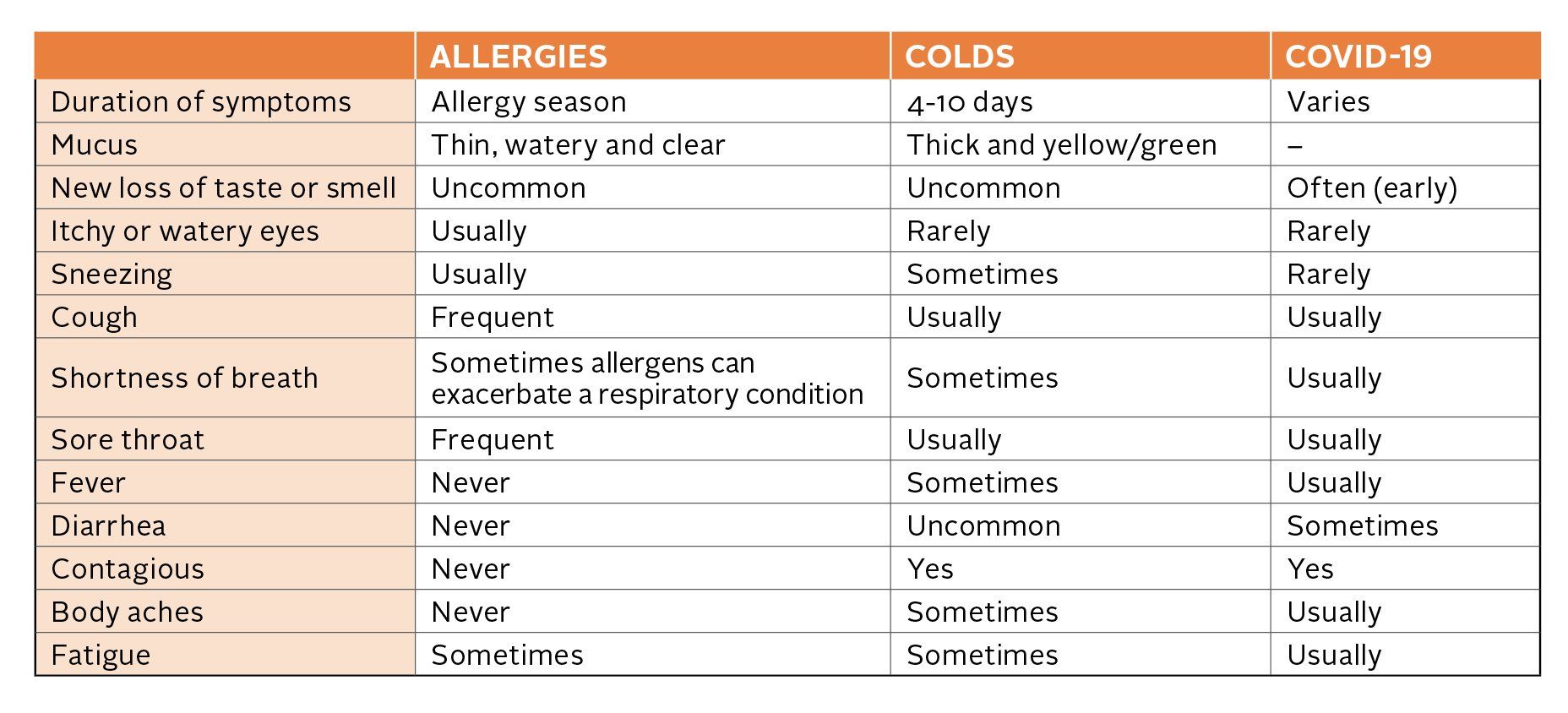
Symptom Checker: Is It Allergies, a Cold or COVID-19?
Not Your Imagination: Pollen Season May Be Getting Worse
According to the American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology (ACAAI), climate change has made pollen season longer and more severe throughout North America. A recent study showed that pollen seasons for plants like trees, grasses, and weeds showed a 20-day increase in length and a 21% increase in pollen concentration from 1990 to 2018. Notably the researchers also found that the pollen produced is more allergenic - more likely to trigger an allergic reaction with fewer grains of pollen in the air.
Sources: Mayo Clinic, ACAAI
Recent Blog Posts